Model of VRP Assumptions (1) The selected locations are known, and
Download scientific diagram | Model of VRP Assumptions (1) The selected locations are known, and the hospital points are also known. (2) The sum of infectious waste material should not be higher than the maximum load of transport vehicles. (3) Each transport vehicle takes the selected location as the starting point, and then returns back to the selected location. (4) The amount of infectious waste is determinate. (5) One vehicle can serve multiple hospitals. (6) Each vehicle travels from node i to j at a speed of 60 kilometers per hour. from publication: Solving a multi-objective location routing problem for infectious waste disposal using hybrid goal programming and hybrid genetic algorithm | Infectious waste disposal remains one of the most serious problems in the medical, social and environmental domains of almost every country. Selection of new suitable locations and finding the optimal set of transport routes for a fleet of vehicles to transport infectious | Goal Programming, Routing and Genetic Algorithm | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
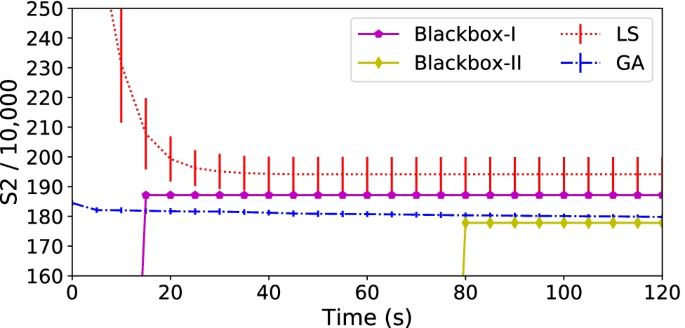
Tackling the rich vehicle routing problem with nature-inspired algorithms
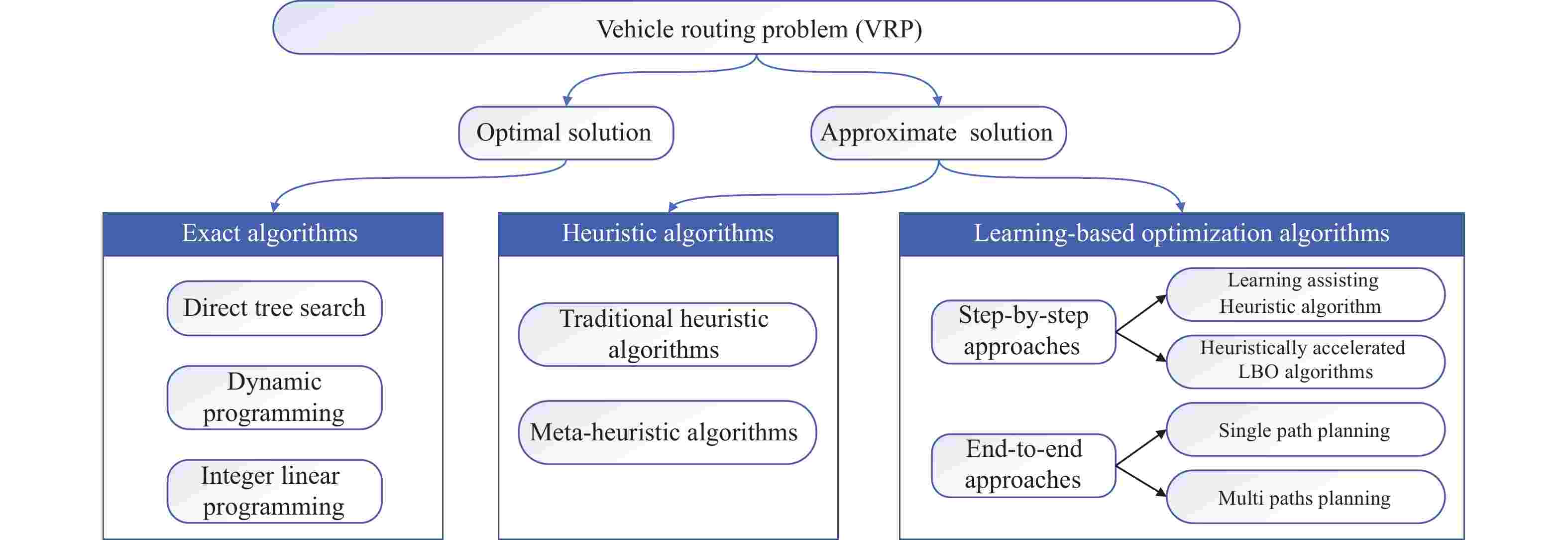
An Overview and Experimental Study of Learning-Based Optimization Algorithms for the Vehicle Routing Problem

Industrial vehicle routing problem: a case study, Journal of Shipping and Trade

Female hunters of the early Americas

Electric Vehicle Routing Problems with Stochastic Demands and Dynamic Remedial Measures
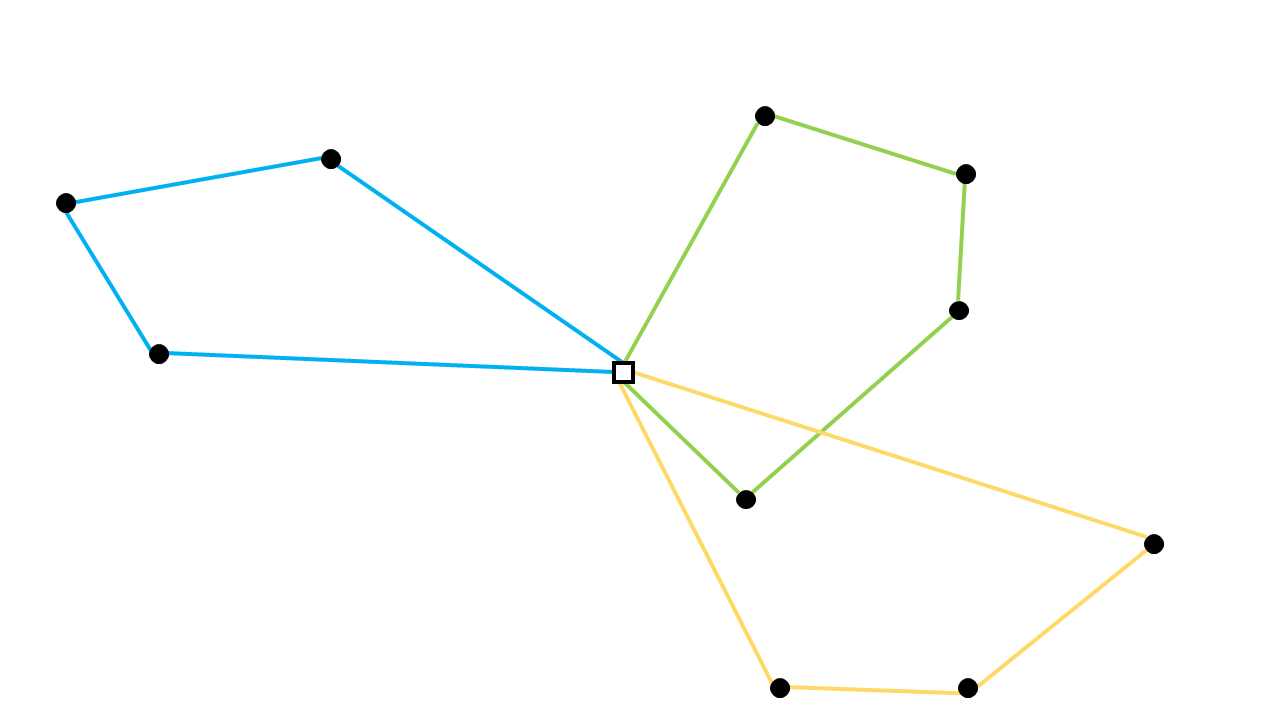
Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem formulation — AIMMS How-To
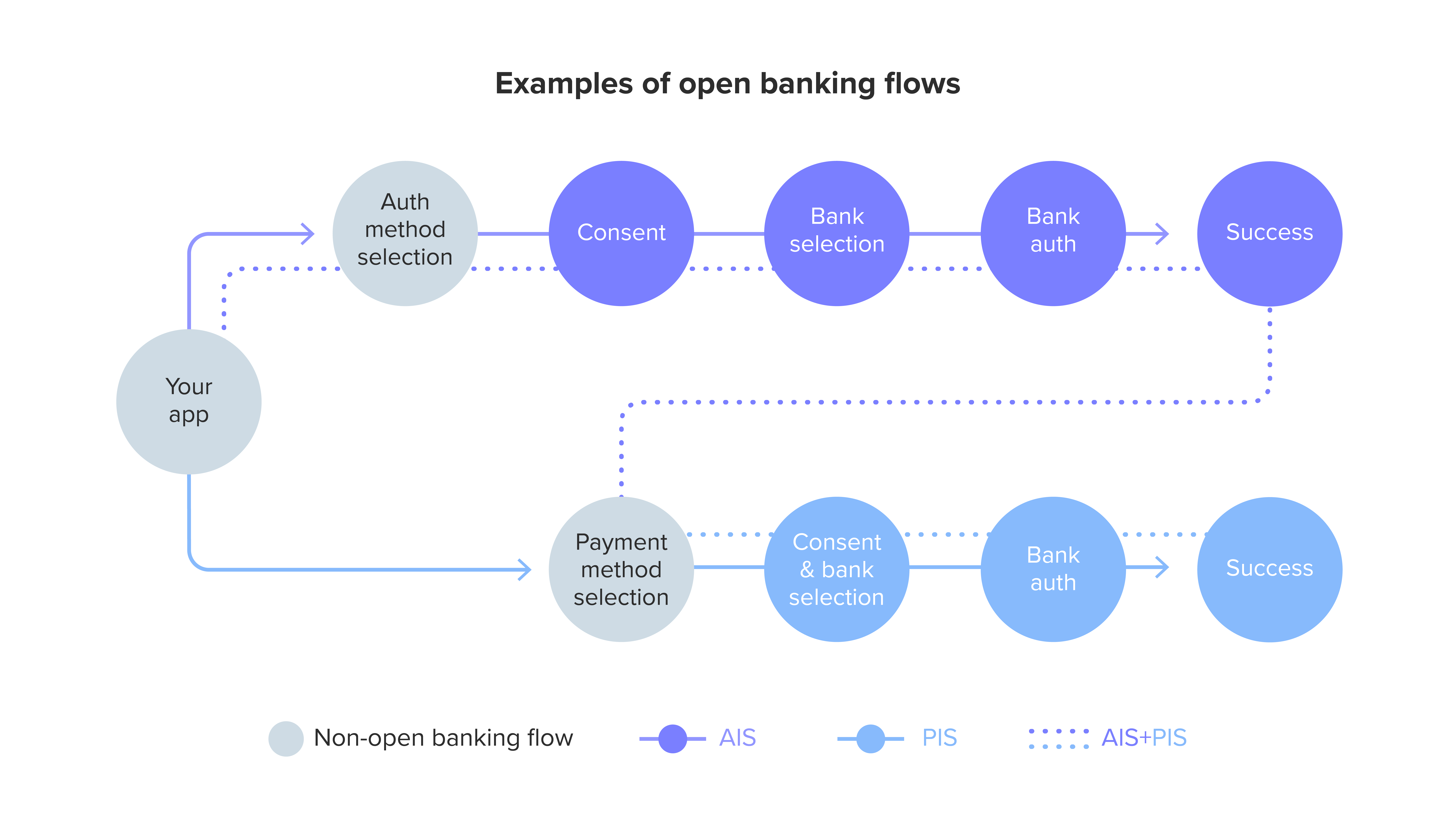
TrueLayer Blog: UX/UI guides: how to optimise your open banking user journey
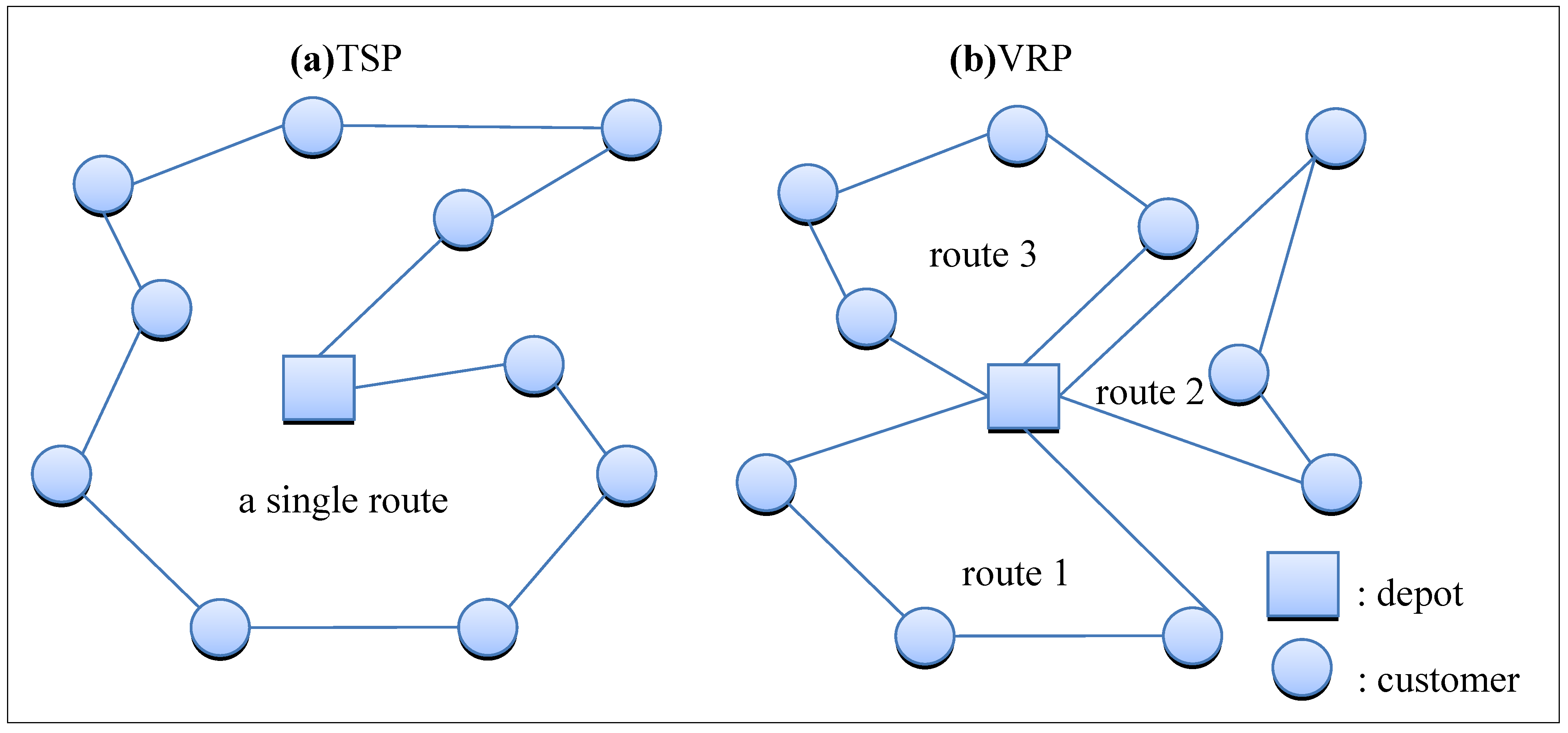
Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Green vehicle routing problem: A state-of-the-art review - ScienceDirect
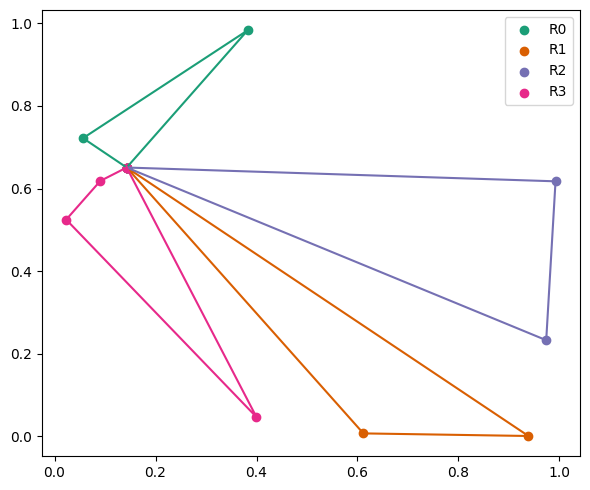
The Vehicle Routing Problem: Exact and Heuristic Solutions, by Bruno Scalia C. F. Leite

OptaPlanner - Vehicle Routing Problem

Comparison of solutions using LINGO13 and hybrid GA

Scheduling the periodic delivery of liquefied petroleum gas tank with time window by using artificial intelligence approaches: An example in Taiwan - Yi-Chih Hsieh, Peng-Sheng You, Cheng-Sheng Chen, 2021









