Multivariate Analysis of Evoked Responses during the Rubber Hand Illusion Suggests a Temporal Parcellation into Manipulation and Illusion-Specific Correlates
The neurophysiological processes reflecting body illusions such as the rubber hand remain debated. Previous studies investigating the neural responses evoked by the illusion-inducing stimulation have provided diverging reports as to when these responses reflect the illusory state of the artificial limb becoming embodied. One reason for these diverging reports may be that different studies contrasted different experimental conditions to isolate potential correlates of the illusion, but individual contrasts may reflect multiple facets of the adopted experimental paradigm and not just the illusory state. To resolve these controversies, we recorded EEG responses in human participants and combined multivariate (cross-)classification with multiple Illusion and non-Illusion conditions. These conditions were designed to probe for markers of the illusory state that generalize across the spatial arrangements of limbs or the specific nature of the control object (a rubber hand or participant’s real hand), hence which are independent of the precise experimental conditions used as contrast for the illusion. Our results reveal a parcellation of evoked responses into a temporal sequence of events. Around 125 and 275 ms following stimulus onset, the neurophysiological signals reliably differentiate the illusory state from non-Illusion epochs. These results consolidate previous work by demonstrating multiple neurophysiological correlates of the rubber hand illusion and illustrate how multivariate approaches can help pinpointing those that are independent of the precise experimental configuration used to induce the illusion.

A) Schematic depiction of experimental setup. Depending on

Group means of frequency of electrical stimulation during the rest
The rubber hand illusion is accompanied by a distributed reduction

Resolving the neural dynamics of visual and auditory scene

A temporal parcellation of the sensory-evoked responses during the
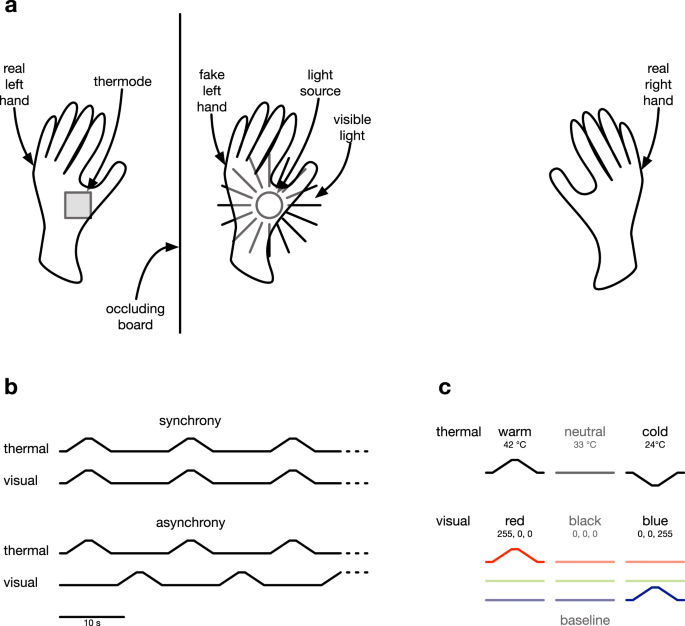
The rubber hand illusion induced by visual-thermal stimulation

Proprioceptive uncertainty promotes the rubber hand illusion

PDF) Multivariate Analysis of Evoked Responses during the Rubber

Figure 1 from The use of realistic and mechanical hands in the rubber hand illusion, and the relationship to hemispheric differences

Cortical areas in which neural word representations predict